What if a single number could show us the UK’s economic health? Let’s explore the complex world of GDP to find out the truth about the UK’s growth. The Office for National Statistics has given us recent data on how we’re doing. But what does this tell us about our future?
The UK’s GDP isn’t just a random number. It shows the deep workings of our economy. Looking at these economic details, we understand past performance and what might happen next.
Experts and government leaders pay close attention to GDP growth. It helps them make plans to improve our economy. By understanding these trends, they make better choices for both the government and businesses. Let’s dive into the details of GDP analysis, using the latest data and advice from experts.
Understanding GDP Growth
Understanding GDP growth is key for deep economic analysis. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) sums up the value of all final goods and services made within a country in a certain period. It shows how well a nation’s economy is doing.
Definition of GDP
GDP means Gross Domestic Product. It’s the full market value of all completed goods and services within a country in a set time. This measure is vital for assessing a country’s economic health and efficiency.
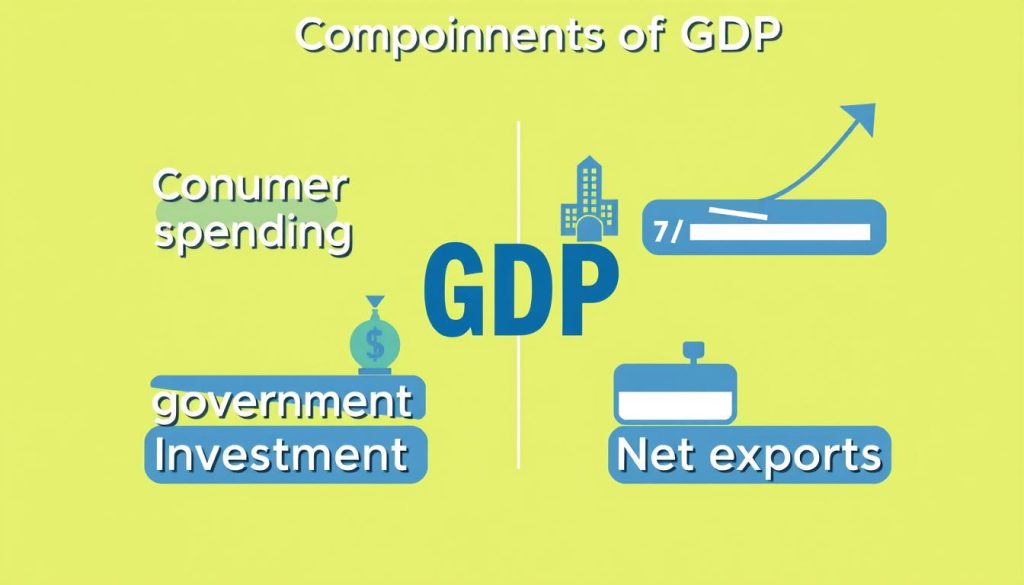
Components of GDP
GDP includes several main parts, known as the GDP components. These are:
- Consumption: The total of all goods and services households buy.
- Investment: Spending on capital goods, inventories, and houses.
- Government Spending: All government expenses on public services and goods.
- Net Exports: A country’s export value minus its imports.
Importance of GDP Growth
GDP growth is crucial for showing economic progress. It signifies an uplift in a country’s national income. When the economy grows, people’s living standards get better. It helps in planning economic analysis and policies. Consistent growth increases investor confidence, leading to more investments.
Historical Trends in UK GDP Growth
The UK’s economic journey is filled with ups and downs, shaping today’s economy. From post-war growth to financial crises, knowing these patterns helps us guess future trends. This knowledge is key for understanding how the economy may grow.
Post-War Economic Boom
After World War II, the UK’s economy grew rapidly. Government initiatives and more spending by people fueled this boom. It set the stage for the growth we see today.
Recessions and Recoveries
But it wasn’t all smooth sailing. The 1970s and early 1990s saw big recessions. During these tough times, the UK made major policy changes. The early 1980s recession, in particular, led to big changes in the economy.
Recent Decades
From the late 20th century to the early 21st century, the UK saw mixed economic results. The late 1990s and early 2000s were good, but the 2008 financial crisis hit hard. Recovery after 2008 was slow, with careful planning by the Bank of England.
Looking at the past, we learn about the UK economy’s growth and what might come next. The way the UK has bounced back from hard times shows it can handle future challenges.
Contribution of Various Sectors to GDP Growth
The UK’s economy grows through the hard work of different sectors. Let’s look at how services, manufacturing, and agriculture help. These sectors boost the economy in their unique ways.
Services Sector
The services sector is the backbone of the UK’s industries. It contributes a huge part to the GDP. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) shows that services like finance, retail, and healthcare are key players. This change shows the UK is moving towards a service-based economy, like many countries worldwide.
Manufacturing Sector
Manufacturing may not be as big as services, but it’s still vital. It has grown thanks to tech and better ways of working. The car, plane, and medicine industries help the economy a lot. They do so by making things more efficiently and innovating.
Agriculture Sector
Agriculture adds a smaller share to the GDP but is crucial for the countryside and food supply. It is getting better with green methods and new tech. Agriculture is adapting by diversifying and focusing on sustainability. It stays important even as the UK modernises.
Government Policies Impacting GDP Growth
The government’s role is key in setting a nation’s GDP growth path. The UK’s economic approaches include fiscal stimulus, rules, and using monetary tools by the Bank of England. Each part is vital for the economy’s shape.
Fiscal Policies
Fiscal strategies are central to economic planning. Adjusting spending and tax rates, the government impacts economic events. For example, boosting public spending in hard times shows how fiscal stimulus can lift GDP. After the 2008 crisis, such government actions helped stabilise the economy.
Monetary Policies
The Bank of England’s monetary techniques, like changing interest rates and quantitative easing, are key for GDP. Lowering rates can boost investment and spending, thus growing the economy. During COVID-19, strong monetary steps were vital to soften the economic blow. These efforts target price stability and job fullness, leading to a healthier economy.
Regulatory Changes
Regulations greatly affect the business scene and thus GDP growth. Policies cutting down excess rules can boost business efficiency and edge. But, too much control may slow growth by upping operational costs. Looking at past policies shows regulation’s varied effects on sectors, underlining the need for thoughtful regulations.
Brexit and its Impact on GDP Growth
Brexit has caused big changes in the UK’s economy. It’s altered trade and foreign investment. Understanding these changes is key to seeing how the UK’s GDP growth is affected.
Trade Relations
Brexit led to new trade talks between the UK and the EU. Making new trade deals has been tough. Now, tariffs and customs are big parts of UK-EU trade.
Businesses are facing more uncertainty. This might slow down trade growth, which would affect the GDP.
Investment Fluctuations
Foreign investment has changed a lot after Brexit. Investors are now more careful due to economic uncertainty. Reports show that foreign investors are hesitating.
Less foreign investment could hurt the economy. It plays a big role in creating jobs, bringing new technology, and keeping the economy stable. The UK’s GDP growth is at risk as investors try to adjust.
Global Economic Influences on UK GDP Growth
Global factors deeply affect the UK’s GDP growth. To grasp these influences, we must look at the country’s trade policies and globalisation effects. This part covers trade agreements, conflicts, and economic globalisation’s impact.
Trade Agreements
Trade agreements are crucial for the UK’s economy. Post-Brexit, the UK has been forming new trade deals worldwide. These agreements help manage global risks and boost growth by improving international trade. They also open up opportunities in new markets, boosting the nation’s GDP.
International Conflicts
Global conflicts affect the UK’s economic stability. They can cause the UK’s GDP to go up and down because of trade disruptions. Economic diplomacy plays a key role in handling these issues, aiming to keep trade peaceful and stable. Conflicts can lead to unpredictable markets, hitting the global supply chain and the UK’s GDP.
Economic Globalisation
Globalisation plays a big part in the UK’s economic scene. It includes merging markets and politics, which impacts GDP growth. The UK benefits from more foreign investments and new technologies. Yet, it faces hurdles like job losses and tough competition.
The global scene brings both chances and challenges for the UK’s growth. By using smart diplomacy and trade, the UK can deal with global risks. This way, it can make the most of globalisation for a stronger economy.
Future Projections for UK GDP Growth
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Bank of England give us insights into the UK’s GDP growth future. These predictions consider tech advances, demographic changes, and possible policy adjustments. It’s a complex picture with many moving parts.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook shows how hard it is to predict in today’s changing global economy. The UK might see some growth, but issues like global trade fights and Brexit could slow things down.
The Bank of England has a detailed take, factoring in inflation goals and policy tweaks. They talk about the need for stability and steady progress. They argue for strong reforms to keep the growth going.
Studies on future economic trends say the UK’s GDP will depend on key challenges. These include integrating new tech and managing an older population. These studies highlight the need for flexible strategies in the face of future economic challenges.
- Technological advancements: Leveraging AI and automation to boost productivity.
- Demographic shifts: Addressing the impacts of an ageing workforce and changing consumption patterns.
- Policy changes: Implementing growth-oriented reforms and maintaining favourable trade relationships.
In the end, economic forecasts look hopeful, but many factors will shape the UK’s growth. Continuous evaluation and adaptable strategies are key to making sure the UK grows economically in the future.
Technological Innovations and GDP Growth
The UK’s economy is changing greatly because of technology, especially in artificial intelligence and automation. These changes help the UK’s GDP grow a lot. It’s important for those making policies and business leaders to understand what this means.
Impact of AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence and automation are changing many industries. AI allows companies to sift through huge data sets and predict outcomes, giving them an advantage. In areas like healthcare and finance, AI helps do repetitive tasks quickly, saving money and making things more efficient. Automation reduces mistakes and keeps quality consistent in making goods, encouraging growth through technology.
- Healthcare: AI is used for better diagnoses, treatment plans, and managing patients, which improves care and efficiency.
- Finance: AI helps in assessing loan applications, spotting fraud, and giving customers tailored financial advice, changing how banks work.
- Manufacturing: Robots on assembly lines and in managing supplies make producing goods faster and with less waste.
Experts in technology predict these advancements could add around £630 billion to the UK’s GDP by 2035.
Role of Digital Economy
The move to digital is also boosting the GDP, showing how key the digital economy is. Using digital platforms makes business simpler and helps reach new markets, increasing economic activity. The UK government is helping this growth by investing in tech companies and improving infrastructure.
- Putting money into digital technologies like 5G makes doing business easier and supports growth.
- Promoting digital skills ensures workers can handle new technologies, keeping the economy strong.
- When tech companies work with schools, it leads to new inventions and practical tech uses.
Studies from economic experts suggest the digital economy might make up to 35% of the UK’s GDP by 2030. This shows how important digital progress is for long-term economic growth.
Labour Market Trends and GDP Growth
Exploring how labour market trends affect GDP growth highlights many important factors. It’s key to match employment rates with job health for strong growth. Looking closely at labour stats shows how more jobs can lift GDP. This is because more workers mean more spending and investing.
How productive the workforce is also matters a lot. When workers do their jobs better, the whole economy benefits. It means we can make more without spending more on costs. Experts say spending on skills and tech helps sectors work better.
Changes in who is working are reshaping jobs, offering both good and tough spots. For example, as more people get older, we need job policies that help them. At the same time, we must get young people ready for work. This balance is crucial for GDP growth, as it affects who can work and how well.
It’s also vital to make sure education keeps up with job needs. Economies today need people with the right skills for now and the future. Putting money into education and ongoing training helps keep the labour force flexible. This is essential for keeping the economy growing over the long haul.
Consumer Spending Patterns and GDP Growth
Consumer spending is changing fast, influencing the UK’s GDP growth greatly. Changes in how we shop, especially with more online purchases, are shifting spending patterns. This is changing the economy.
Retail Sector
The UK’s retail sector shows what consumers are doing. It’s a big part of the economy. A rise in retail sales suggests a strong economy. Stores are mixing in-store and online shopping to meet new demands.
Online Shopping Trends
E-commerce has really changed retail. More people buying online shows how big its impact is. Reports show online sales growing, as shoppers look for ease, variety, and deals.
This move to online shopping is pushing retail to be more digital. It’s also helping the UK’s economy grow.
Investment Strategies to Boost GDP Growth
Public and private investments are key to boosting GDP growth. They make the economy more stable and help it progress.
Public Investment
Public investment is vital for developing infrastructure, which is essential for a country’s economic growth. The government spends money on transport, health care, and education. This has helped the economy grow.
For instance, the UK has spent money on improving railways and digital networks. These investments help businesses grow and create jobs, boosting the economy.
Private Sector Investment
Investing in the private sector is also important for economic growth. Tax breaks and grants encourage businesses to spend on research and growth. This can attract more investment from abroad, helping the GDP grow.
Successful partnerships between the public and private sectors show how working together can speed up economic growth. Such collaborations can lead to more confidence among investors.
- Enhanced infrastructure through public spending
- Incentives for private sector investment
- Public-private partnerships
To sum up, we need both public spending and private investment to keep the economy growing. Looking at history and case studies shows us this dual approach works well.
Impact of Environmental Policies on GDP Growth
In the United Kingdom, focusing on sustainable development is key. The influence of green policy on the economic growth is clear. This big change towards a greener economy is updating different sectors. It boosts the economy and protects the environment at the same time.
Green Economy
The rise of a green economy in the UK shows how looking after the environment helps the economy grow. The government’s green policies strive to achieve economic and environmental goals together. Studies show that investing in green tech and eco-friendly habits greatly boosts the economy. This not only cuts environmental harm but also creates jobs and sparks new ideas in businesses.
Renewable Energy Sector
The growth of the renewable energy sector is crucial for the UK’s eco-friendly economic development. Energy from wind and sun is becoming more popular than old energy sources. This is because of a focus on saving the planet through economics. Big investments from both the government and businesses have improved energy use. They’ve also cut down on pollution.
Studies on the economy show that the renewable energy field does more than just make the country’s energy better. It boosts the country’s economy by creating lasting jobs and green businesses.
Role of Education and Skills Training in GDP Growth
Education and skills development are key to improving a country’s economy. They help raise productivity and get the workforce ready. This section looks at how higher education and training programs greatly affect the economy.
Higher Education
Higher education gives people the knowledge and skills for better jobs. Universities and colleges offer tough courses that push students to grow. This helps them do well in their careers.
Studies show that countries with more people in tertiary education grow faster. Higher education makes sure graduates can meet today’s job market needs.
Workforce Training Programs
Training programs also boost productivity and keep the economy moving. These programs, supported by governments and businesses, teach important skills quickly. They target skills needed for jobs right now.
Government reports say these training sessions cut unemployment and grow the skilled workforce. Readiness assessments show they massively improve work performance. This leads to higher economic productivity.
Challenges to Sustaining GDP Growth
Keeping the UK’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growing steadily is tough. Economic inequality and inflation are big worries for those making policies. These issues affect how people spend, save, and the whole economy’s health. They’re important for keeping GDP growth on track.
Economic Inequality
Economic inequality means not everyone gets the same slice of the wealth pie. It’s bad for spending and for people moving up economically. When too much wealth goes to a few, most people have less to spend. This can slow down the economy. Finding ways to share wealth more fairly is key to better growth.
Inflation
Inflation makes everything pricier, hurting how far our money goes. It messes with interest rates and market stability. Reports say that changing inflation rates make business hard to predict. This can stop investments and slow the economy. Keeping inflation in check helps everyone and keeps the economy growing.